Setting Up a Local Load Balancer Using NGINX and Flask on WSL
By Sharan Panthi
#load balancer#Local Load Balancer#NGINX#Flask#WSL#traffic distribution#local setup
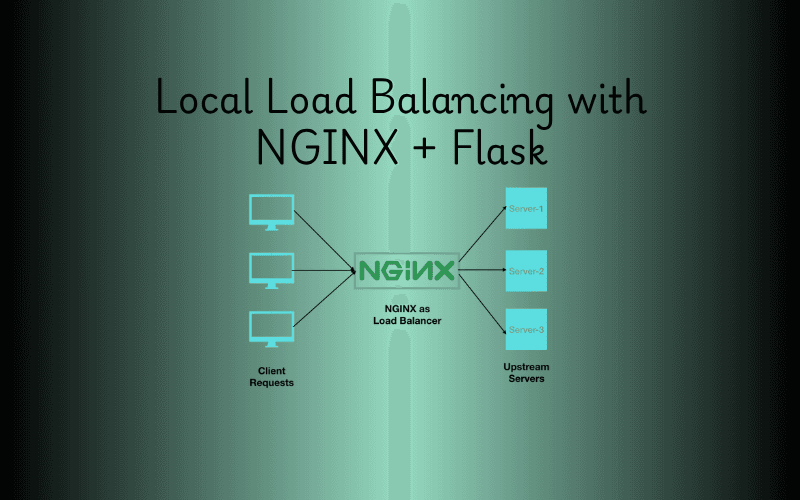
Imagine you’re running a busy website, and suddenly, traffic spikes. One server can’t handle it all—requests slow down, and users get frustrated. That’s where a load balancer comes in, distributing traffic across multiple servers to keep things running smoothly. In this guide, we’ll set up a simple local load balancer using NGINX and two Flask applications on WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux). It’s a fantastic way to learn load balancing hands-on, right on your own machine!
Context
- NGINX: A high-performance web server that doubles as a reverse proxy and load balancer. It’s widely used for its speed and ability to manage traffic efficiently.
- Flask: A minimalist Python web framework perfect for building lightweight web apps or APIs.
- WSL: A feature of Windows that lets you run a Linux environment (like Ubuntu) without a separate machine or virtual machine, making it ideal for development.
By combining these tools, you’ll create a mini load-balanced system where NGINX directs traffic between two Flask servers. Let’s dive in!
🧰 Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
- WSL installed (Ubuntu recommended)
- Python 3
- Internet connection (for package downloads)
- Basic Linux command knowledge
